General guidelines for iSCSI deployment for inSync Storage
About iSCSI
Block I/O is the basic mechanism for DISK access using the SCSI protocol as the command set. Block I/O is fast and data can be transmitted in various block sizes like 2K, 4K, 8K, 16K, 64K, 128K etc. Block I/O can be done over various transports. Parallel SCSI cables, copper fiber, optical fiber and even encapsulated and transmitted over IP networks (iSCSI).
Block I/O is what is used to talk to DISKS. By carrying SCSI commands over IP networks, iSCSI is used to facilitate data transfers over intranets and to manage storage over long distances.
Following is the general guide line for iSCSI deployment:
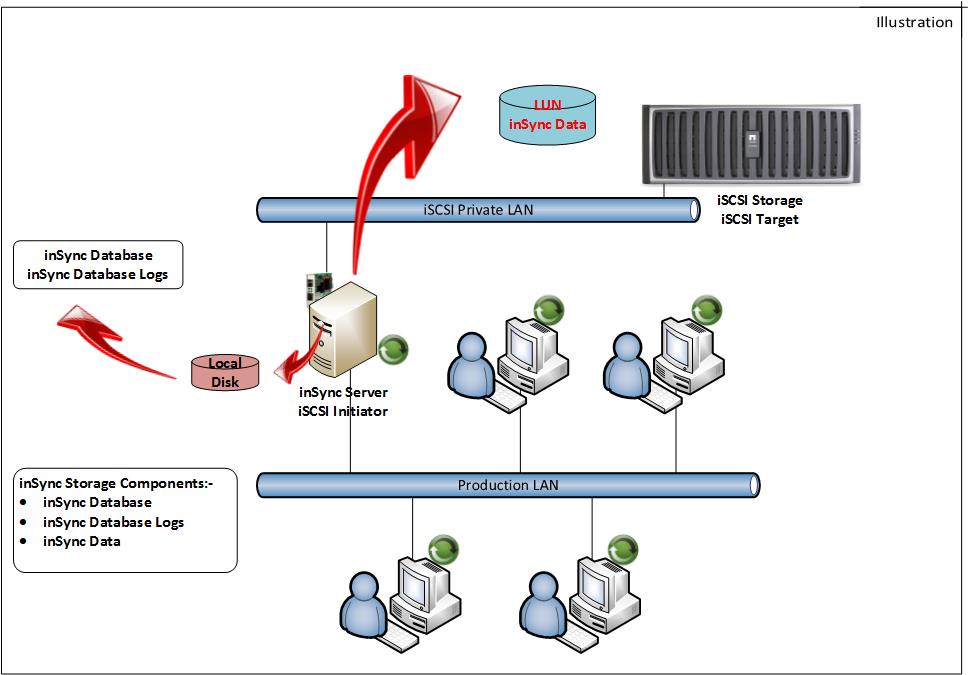
iSCSI performance for inSync Storage can be enhanced by the below mentioned ways:
- Use dedicated private network for iSCSI communication.
- Deploying Ethernet NICs with TCP/IP offload engine (TOE) features to reduce the CPU demands for iSCSI command processing.
- Most of the iSCSI SAN operates at 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps, it is recommended to have minimum of 1 Gbps connectivity from iSCSI initiator to target.
- iSCSI performance may also be influenced by the choice of software-based iSCSI initiators or purpose-built iSCSI HBAs, instead of a conventional NIC or use of Fiber channel.
Note: inSync Storage database and database logs must be stored on the local disk to avoid possible network latency.

