General guidelines for NFS share based deployment for inSync Storage
Summary
NFS or Network File System, is a server-client protocol for sharing files between computers on a common network, generally used for Linux systems. NFS enables you to mount a file system on a remote computer as if it were local to the system. You can then directly access any of the files on that remote file system. The server and client do not have to use the same operating system. The client system just needs to be running an NFS client compatible with the NFS server.
Below are a few key points to be noted while configuring inSync storage on an NFS share:
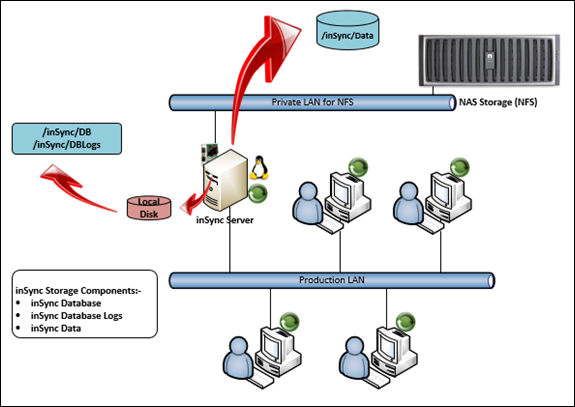
- Only the Data component of inSync storage can be configured on a NFS share.
- The Database and Database logs will have to be configured on local or internal disks.
- To avoid any read/write delays, place the NFS server and inSync server in a single hop, dedicated network.
- NFS share, if used on Linux, should be configured for auto-mount at server boot/reboot by adding an entry in/etc/fstab.
- The ownership & read/write permissions of the NFS share directory should be set to user insyncserver and group insyncserver (insyncserver is the user created on the inSync server).
- Ensure that the Storage directories are not shared/accessed by any other user/system.
- Enable NFS client logging to log mounts & other critical events (useful for troubleshooting).
- Disk caching is recommended to be disabled.
Note: NAS is supported, but not recommended because of possible latencies and throughput restrictions imposed by the network, which may cause performance issues.
Below is an illustration of NAS (Network Attached Storage) based NFS storage being used for inSync storage Data:
Here is an external reference on how to setup NFS server and client:
http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/centos-fedora-rhel-nfs-v4-configuration/

