User Guide - Preparing the environment for successful Druva File Server Restore
One-stop solution
This document provides a clear, step-by-step guide that focuses on how to prepare and configure restore of files & folders. Follow these instructions to effectively manage your restore using Druva File Server Agent
Note: Before you go ahead with the information shared in this restore user guide, make sure you have configured the backups and they are successful.
Purpose
Prepare the environment for Druva File Server Agent to have successful restore of Files & Folders
Windows Operating System
- ►1. What is a file server?
-
- A file server is a server responsible for the storage and management of data files so that other computers on the same network can access the files.
- It enables users to share information over a network without having to physically transfer files.
- It can store various types of data, such as executables, documents, photos, and videos.
- It has an operating system, system state, files, and folders (Data).
- ►2. What are RPs ( Recovery Points) in File server?
-
- An RP (Recovery Point) is the cumulative data stored on the Druva cloud, arranged by the date of backup.
- When you select any RP for restore, it is capable of a full restore.
- RPs are created only for backup with states - Successful & Successful with Errors, NOT for Failed, skipped, Queued, or canceled.
- Availability of the RP depends upon retention set in the backup policy .
- ►3. Where can RPs (Recovery Points) be viewed for File server?
-
- Go to the Management Console - select your organization - Protect - File server - Registered Servers - Click on the server name - Under Configured backup sets - Check the square box besides the backup set name - Click on Restore button
- Expand the dates and select the dates for which restore needs to be performed.
- ►4. What are the Types of RP (Recovery Points) ?
-
- The RP’s are differentiated based on where it has been stored.
- There are 3 type of RPs: For more detailed information on RP's (Click Here)
- Hot recovery point
- Warm recovery point
- Cold recovery point
- ►5. What is the Restore Workflow for the File Server?
-
For more information on the file server restore workflow (Click Here)
- Administrator initiates a restore operation.
- Druva checks if Hybrid Workloads agent is running.
- Druva validates the restore destination.
- Druva checks the free space available at the restored destination.
- Druva identifies the file sets for restore.
- Druva starts the restore operation and sequentially downloads the filesets to the restore destination
- ►6. What are the types of restore for file servers?
-
There are 2 types of restore methods:
- Restore to Original Location :
- Select this option if you want to restore the selected files to its original location.
- Restore to Alternate Location:
- Select this option if you want to restore the selected files to an alternate server.
- Restore to Original Location :
- ►7. What are the prerequisites for a successful restore?
-
- Verify the pre-checks on the target server where the Files need to be restored.
- Connection
- Verify the connection between the server and Druva.
(Use command prompt or powershell)
- Verify the connection between the server and Druva.
- Service
- The service “Hybrid Workloads agent” should be in Running mode.
(start-run-services.msc)
- The service “Hybrid Workloads agent” should be in Running mode.
- UI Status
- The status of the target FileServer on Druva console should show as “Connected”.
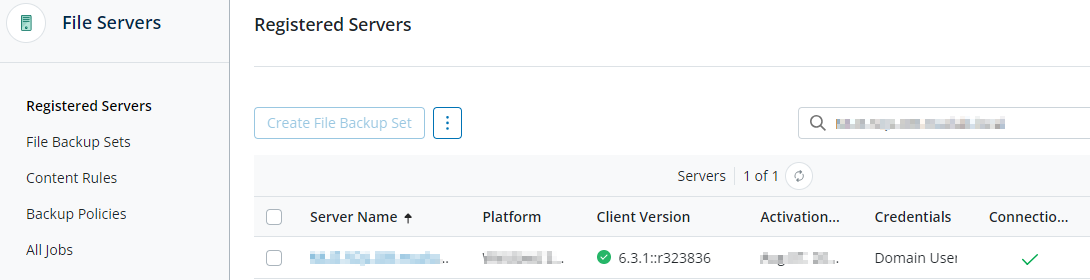
- The status of the target FileServer on Druva console should show as “Connected”.
- Anti-Virus
- Druva executables should be added to the exclusions of Anti-virus.
(If not done, the anti-virus keeps the .exe on HOLD and the backup will stay in Queued state)
- Druva executables should be added to the exclusions of Anti-virus.
- VSS Writers and Provider
- In case you have a hardware provider, you can change it for backups.
- (once the setting is in place, Druva will use this provider for backups)
- VSS writers should be stable. Verify the same in command prompt (Admin mode)
vssadmin list writers - You can set VSS to write shadow copies to a separate NTFS volume, in case you want to change the snapshot volume, where data is snapshot temporary.
- Operating System checks
- Check the available disk space on the target server.
- If the source data which has been backed up Windows deduplication enabled volume, do make sure that the restore target server should also have Windows deduplication enabled on the restore Volume. Or else the restore data would be bigger in size compared to the source data.
- FAQs - General questions about File servers
- ►8. How to Perform a File Server Restore?
-
- Go to the Management Console - select your organization - Protect - File server - Registered Servers - Click on the server name - Under Configured backup sets - Check the square box besides the backup set name - Click on Restore button
- Expand the dates and select the dates for which restore needs to be performed.
- Step-by-step instructions to restore file server data (Click Here)
- ►9. Do / Don’ts for File server
-
- You can only restore data to a server that has the same operating system as the source server.
- File Server restore does not support Cross Platform restore (Windows to Linux or vice versa.)
- If you restart or reboot your servers during a restore, the restore operation restarts from scratch.
- Restores are not supported to the mapped drives.
- Click Here to know more on Do/Donts
Linux Operating System
- ►1. What is a file server?
-
- A file server is a server responsible for the storage and management of data files so that other computers on the same network can access the files.
- It enables users to share information over a network without having to physically transfer files.
- It can store various types of data, such as executables, documents, photos, and videos.
- It has an operating system, system state, files, and folders (Data).
- ►2. What are RPs ( Recovery Points) in File server?
-
- An RP (Recovery Point) is the cumulative data stored on the Druva cloud, arranged by the date of backup.
- When you select any RP for restore, it is capable of a full restore.
- RPs are created only for backup with states - Successful & Successful with Errors, NOT for Failed, skipped, Queued, or canceled.
- Availability of the RP depends upon retention set in the backup policy .
- ►3. Where can RPs (Recovery Points) be viewed for File server?
-
- Go to the Management Console - select your organization - Protect - File server - Registered Servers - Click on the server name - Under Configured backup sets - Check the square box besides the backup set name - Click on Restore button
- Expand the dates and select the dates for which restore needs to be performed.
- ►4. What are the Types of RP (Recovery Points) ?
-
- The RP’s are differentiated based on where it has been stored.
- There are 3 type of RPs: For more detailed information on RP's (Click Here)
- Hot recovery point
- Warm recovery point
- Cold recovery point
- ►5. What is the Restore Workflow for the File Server?
-
For more information on the file server restore workflow (Click Here)
- Administrator initiates a restore operation.
- Druva checks if Hybrid Workloads agent is running.
- Druva validates the restore destination.
- Druva checks the free space available at the restored destination.
- Druva identifies the file sets for restore.
- Druva starts the restore operation and sequentially downloads the filesets to the restore destination
- ►6. What are the types of restore for file servers?
-
There are 2 types of restore methods:
- Restore to Original Location :
- Select this option if you want to restore the selected files to its original location.
- Restore to Alternate Location:
- Select this option if you want to restore the selected files to an alternate server.
- Restore to Original Location :
- ►7. What are the prerequisites for a successful restore?
-
- Verify the pre-checks on the target server where the Files need to be restored.
- Connection
- Verify the connection between the server and Druva.
(Use command prompt or powershell)
- Verify the connection between the server and Druva.
- Service
- The service “Phoenix” should be in Running mode.
(etc/init.d/Phoenix status)
- The service “Phoenix” should be in Running mode.
- UI Status
- The status of the target FileServer on Druva console should show as “Connected”.

- The status of the target FileServer on Druva console should show as “Connected”.
- Anti-Virus
- Druva executables should be added to the exclusions of Anti-virus.
(If not done, the anti-virus keeps the .exe on HOLD and the backup will stay in Queued state)
- Druva executables should be added to the exclusions of Anti-virus.
- Operating System checks
- Check the available disk space on the target server.
- FAQs - General questions about File servers
- ►8. How to Perform a File Server Restore?
-
- Go to the Management Console - select your organization - Protect - File server - Registered Servers - Click on the server name - Under Configured backup sets - Check the square box besides the backup set name - Click on Restore button
- Expand the dates and select the dates for which restore needs to be performed.
- Step-by-step instructions to restore file server data (Click Here)
- ►9. Do / Don’ts for File server
-
- You can only restore data to a server that has the same operating system as the source server.
- File Server restore does not support Cross Platform restore (Windows to Linux or vice versa.)
- If you restart or reboot your servers during a restore, the restore operation restarts from scratch.
- Restores are not supported to the mapped drives.
- Click Here to know more on Do/Donts

