Getting started with configuring virtual machines for backup
 Business
Business  Enterprise
Enterprise  Elite
Elite
Overview
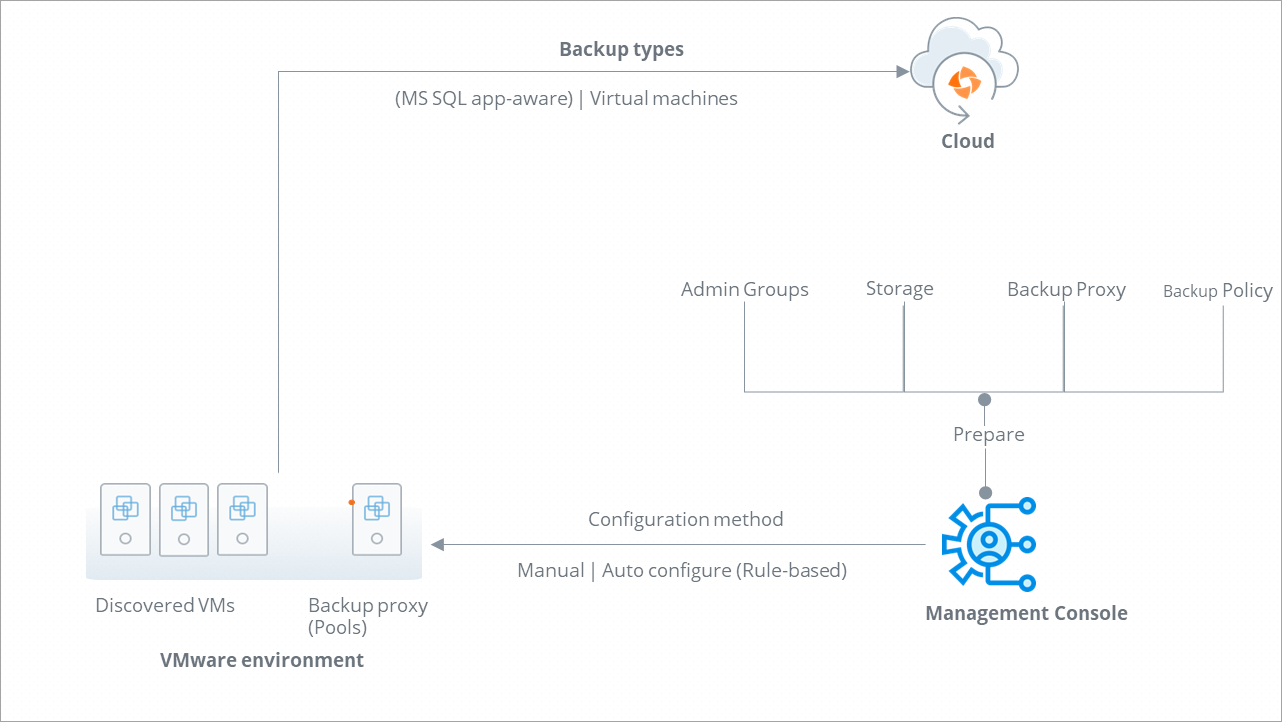
After registering your VMware setup with Druva, Druva discovers the virtual machines that are available in your VMware environment with the help of a backup proxy and lists them in the Management Console.
Step 1: Decide the backup scope
As an administrator, you can configure virtual machines for:
-
Full backup
-
Application-aware backup. Currently, Druva supports SQL Server application-aware backups.
-
Instant Restore
Note: The type of backup needs to be specified in the backup policy. The default backup policy is configured for non-application-aware backup.
Step 2: Prepare
Before you configure your virtual machines for backup, you have to:
-
Decide the virtual machines you want to backup.
-
Decide the region where you want to store the backups. You cannot change storage later.
-
Decide to use the default or create a new administrative group.
Administrative groups are formed to simplify server management. It is a logical categorization of servers and virtual machines that share similar attributes. Servers can be grouped based on similar attributes like server type, server location, and operating system.
See, Manage administrative groups. -
Decide to use the default or create a backup policy.
A backup policy is a set of rules that defines the schedule for automatic backups that occur on virtual machines configured for backup.
See, Manage backup policy. -
If you want to store your backups in local storage, configure the CloudCache. For more information, see Configure CloudCache.
-
If you want to restore the virtual machines instantly, make sure that you map the virtual machines to a supported CloudCache(Linux only).
-
Instant restore and migrate to production jobs support staging datastores. A staging datastore is a datastore on an ESXi host that stores all changes to the instantly restored virtual machine.
-
Migrate to production job for a VM cannot reuse the staging datastore used for the instant restore job of that VM. If you want to migrate a virtual machine to production, ensure you have another datastore on the same or different ESXi host, depending on whether you are migrating to the same or alternate host.
-
Review the prerequisites for configuring virtual machines for backup.
Step 3: Configure VMs for backup
You can configure the virtual machines for backup using one of the following methods:
-
Manually
For more information, see Manually configure virtual machines for backup -
Automatically
You can automatically configure virtual machines for backup by creating rules in the Management Console.
An auto-configuration rule maps to a view or object in the vCenter to the specified storage (Druva storage in the AWS region), an administrative group, a backup policy, and a backup proxy pool.
Based on the auto-configuration rule, any object that is not configured in the view gets automatically configured as per the rule definition.
For more information, see Auto configure virtual machines for backup.

