Quarantining virtual machines resources
 Business
Business  Enterprise
Enterprise  Elite
Elite
Overview
If a VMware virtual machine that you've been backing up with Druva is afflicted by ransomware, you can immediately contain the spread and recover from the attack. The Ransomware Recovery service by Druva allows you to quarantine all the affected recovery points of this virtual machine. Once you quarantine a recovery point, you cannot restore any data from it, limiting the scope of the ransomware attack as a consequence. For more information on quarantining a VMware resource, editing the quarantine range, un-quarantining a recovery point, or deleting quarantined recovery points, see Ransomware Recovery for VMware.
This article explains the impact quarantining a recovery point has on virtual machine restores, MS SQL point in time restores, or VMware instant restores. It also describes how the Druva computes the quarantine range.
Restores from quarantined recovery points and quarantine range
You cannot perform VM restores, MS SQL restores, and VMware Instant Restores from quarantined recovery points. You can only restore from recovery points that are deemed safe and haven’t been quarantined in Ransomware Recovery.
Note: The Files and Folders hierarchy view is not displayed in the restore dialog box if you perform a VM Restore from a quarantined recovery point. A recovery point needs to be mounted before the files and folders list can be displayed. Druva blocks mounts of quarantined recovery points.
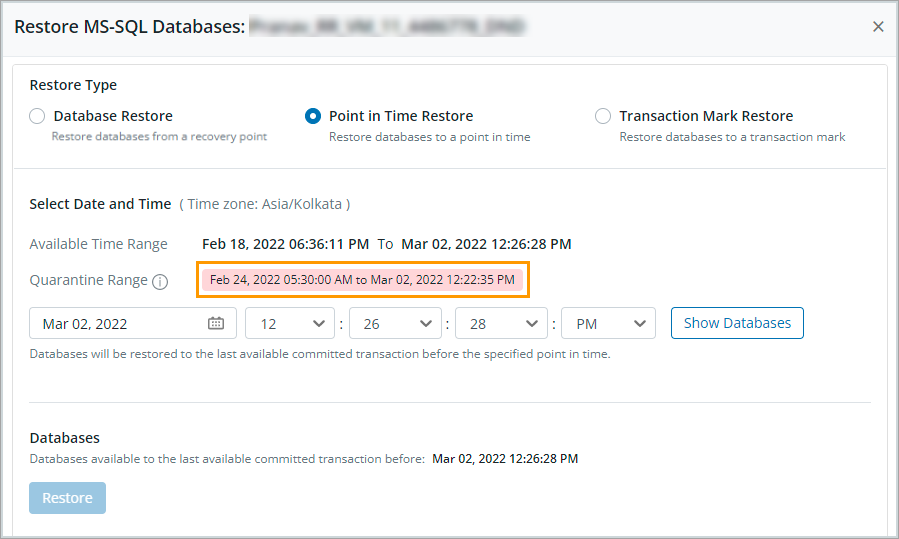
The quarantine range displayed on the Restore MS SQL Databases page for SQL Point in time and Transaction Mark Restores may be larger than the quarantine range defined in Ransomware Recovery. Here is why: During a SQL point in time restore, Druva first restores the recovery point created for the full backup and then restores all the recovery points created for log backups. If any recovery point is quarantined in Ransomware Recovery, Druva automatically quarantines all recovery points linked with the quarantined recovery point. This makes the quarantine range in Druva larger than the range specified in Ransomware Recovery.
For Transaction Mark Restores, Druva does not consider the transaction mark creation time but quarantines all the recovery points linked to the quarantined marked transaction log. Again as a consequence, the quarantine range in Druva becomes larger than the range specified in Ransomware Recovery.
The extended quarantine range is computed as follows:
| Recovery point quarantined from Ransomware Recovery | Quarantine range in Druva includes |
|---|---|
| Recovery point associated with a full backup | The full backup recovery point and all associated log backup recovery points. |
| Recovery point associated with a log backup | The log backup recovery point and all subsequent log backup recovery points. |
| No recovery points found in the quarantined range | All log backup recovery points created after the quarantined range. |
In the following example, we quarantined full and log backup recovery points for a VMware resource in Ransomware Recovery from February 24, 2022, to February 26, 2022.
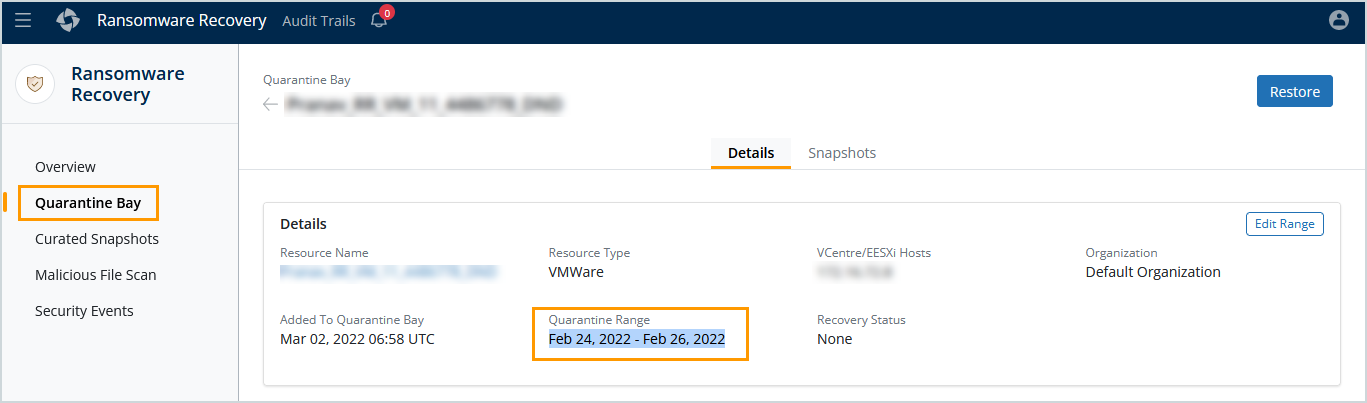
The quarantine range displayed in Druva is from February 24, 2022, to March 02, 2022. The quarantine range is larger than the ransomware recovery range because, in addition to the quarantined recovery points, all linked log backup recovery points have been quarantined as well.