VMware functionalities
 Business
Business  Enterprise
Enterprise  Elite
Elite
Changed Block Tracking
VMware provides the Changed Block Tracking (CBT) capability that Druva uses to analyze and backup virtual machines in an optimal way.
CBT is a VMware feature that helps perform incremental backups. CBT identifies and tracks block changes since the last backup, and stores these changes in log form. This translates to increased backup speeds, reduced backup window, and reduced size of data being transferred.
The Auto-enable CBT feature provides a way to automatically enable CBT for configured virtual machines through Druva instead of an administrator doing it manually. The CBT setting is part of backup policy. Druva will try to enable CBT before the backup schedule kicks in for virtual machine(s). There should be no user recovery points on the virtual machine for this feature to work. In case there are user recovery points present on the virtual machine, Druva will run a full scan to backup the changed blocks. To know more about CBT, see Changed Block Tracking in the VMware documentation library.
Note:
- By default, the CBT option is enabled in the Druva backup policy.
- If CBT(Change Block Tracking) is enabled, Thin disk are restored as Thin disk.
- If CBT is disabled Thin disk are restored as Thick Disk Eager Zeroed.
- Thick Disk (Both Eager and Lazy Zeroed) are always restored as Thick Disk Eager Zeroed.
- CBT status remains unchanged if a virtual machine is restored to the original location. If a virtual machine is restored to an alternate location, CBT is disabled.
- You may see VMWARE_VMOMI13 error if the CBT of virtual machine is not set correctly and the backup proxy version is less than 4.4. For more information on the error, see VMware VMOMI errors.
- The source data size or changed data size is determined based on the size reported by the CBT APIs of VMware.
The virtual machines list on the Management Console is updated when you deploy and register the first backup proxy on the hypervisor. This list includes the CBT status of the virtual machines hosted on the hypervisor and is refreshed every 24 hours after the backup proxy is registered. You can click the refresh button on the Management Console to manually update the CBT status of the virtual machines.
Note: Clearing the "Auto-enable CBT" check box does not imply that CBT is disabled for virtual machine. The "Auto-enable CBT" option is only for auto enablement of CBT and not to disable CBT .
The following table illustrates the CBT state and the systems expected behavior:
| Situation | Expected Result |
|---|---|
| If CBT is disabled and " Auto‐enable CBT" : Yes | |
|
Recovery points present |
Run full scan of virtual machine(s). |
|
Recovery points not present |
Enable CBT and read changed blocks for incremental backup. If for some reason Druva is not able to enable CBT, backup will fail. |
| If CBT is disabled and " Auto‐enable CBT" : No | |
|
Recovery points present |
Run full scan of virtual machine(s). |
|
Recovery points not present |
Run full scan of virtual machine(s). |
| If CBT is previously enabled correctly, Auto-enable CBT --> Yes OR No | |
|
Recovery points present |
Read changed blocks for incremental backup. |
|
Recovery points not present |
Read changed blocks for incremental backup. |
| If CBT is enabled but in inconsistent state and "Auto‐enable CBT": Yes | |
|
Recovery points present |
Run full scan of virtual machine(s). |
|
Recovery points not present |
CBT is reset and read changed blocks for incremental backup. |
| If CBT is enabled but in inconsistent state, and "Auto‐enable CBT": No | |
|
Recovery points present |
Run full scan of virtual machine(s). |
|
Recovery points not present |
Run full scan of virtual machine(s). |
Note: Do not run the vmcontrol command and auto enable CBT run simultaneously.
To know if Druva is running a full scan, view the progress log for the job. The following is an example of the progress log for a full scan:
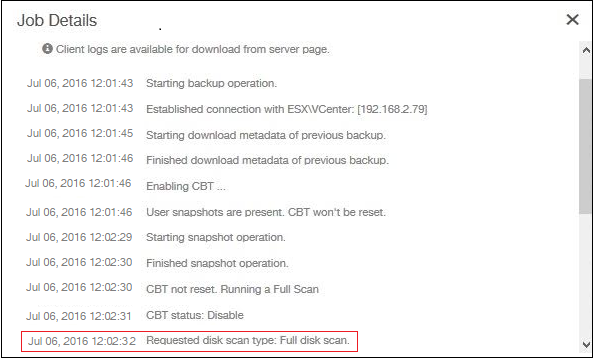
Reset CBT
To reset CBT using vmcontrol untility, see Use the vmcontrol utility to enable CBT.
Edit CBT options
You can edit the CBT options when you:
VMware Tools Quiescing
VMware Tools is an optional set of drivers and utilities provided by VMware to enhance the performance of the guest operating system on a virtual machine and improve interaction between the guest and the host server. The tool also provides the ability to take quiesced recovery points of Windows guest OS in conjunction with Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS).
VMware Tools is mandatory if you want Druva to run Microsoft SQL Server aware backups on VMware VMs.
Druva 'Enable VMware tools quiescing' setting provides the capability to enable or disable VMware tools quiescing if the tools are installed on the system. This functionality will ensure backups will still run by disabling the quiescing flag in case VMware tools are broken on your system. The quiesce setting is part of the backup policy. If enabled, Druva will take an application-consistent recovery point. If disabled or VMware tools not installed or running, the backup will still succeed with a crash-consistent recovery point. You can select the Fallback to crash consistent backup option to capture a crash-consistent recovery point if quiescing of snapshot fails for reasons such as VM tools not installed/running/updated or VSS services-related issues on Guest OS and the backup fails.
For more information, see Manage backup policy and Reconfigure virtual machines configured for backup.
Note: By default, the quiescing option is enabled and Fallback to crash consistent backup option is disabled in the Druva backup policy.
The following table illustrates the state of VMware tools and the systems expected behavior:
| Enable VMware tools Quiescing | Select Fallback to crash consistent | VMware tools installed | VMware tools running | VSS Service (Windows only) | Recovery point attempted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Crash-consistent - No Quiescing |
| Yes | Yes/No | No | N/A | N/A | Crash-consistent - No Quiescing |
| Yes | Yes/No | Yes | No | N/A | Crash-consistent - No Quiescing |
|
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Disabled |
|
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Disabled | Crash-consistent - No Quiescing |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Enabled | Application consistent - with Quiescing This is mandatory for Microsoft SQL Server aware backups. |
|
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Enabled |
Application consistent - with Quiescing This is mandatory for Microsoft SQL Server aware backups. |
Edit options for VMware Tools Quiescing
You can edit the VMware Tools Quiescing options when you:

