About disaster recovery for VMware virtual machines
Enterprise Workloads Editions
❌ Business| ✅ Enterprise (Purchase Separately) | ✅ Elite
Overview
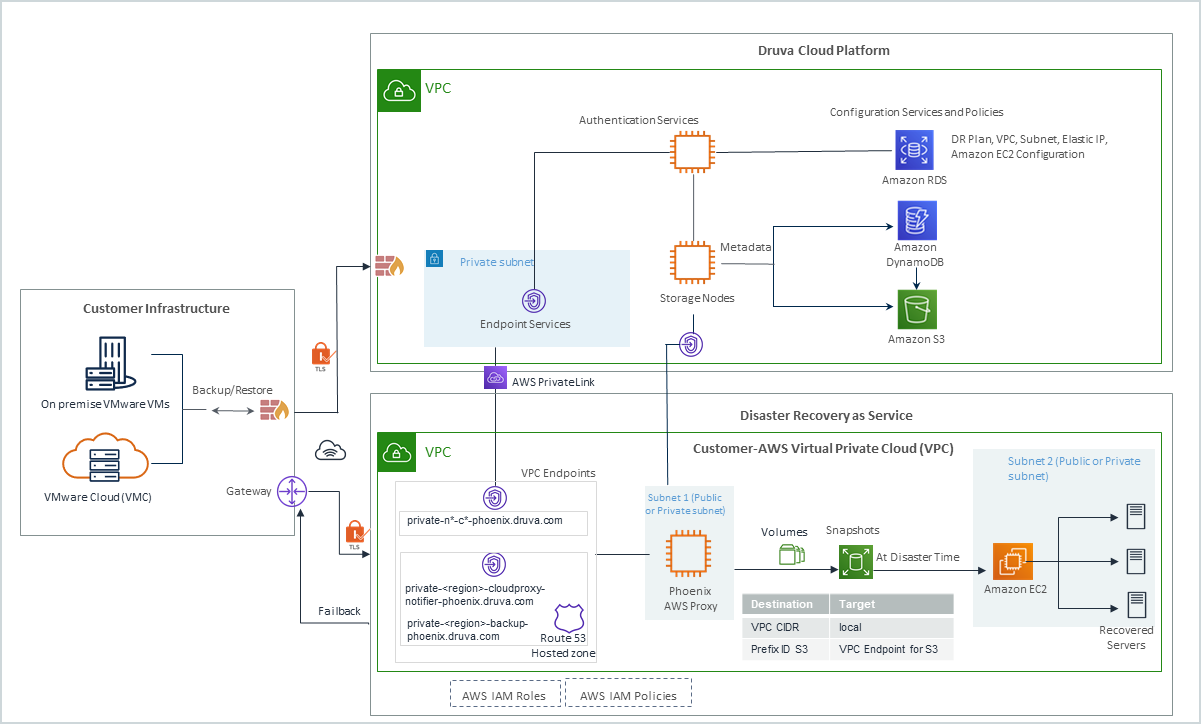
Druva introduces the disaster recovery functionality to extend its converged cloud-based data protection solution for enterprise infrastructure. The Disaster Recovery functionality enables you to recover and spin up the already backed up virtual machines in the Amazon Web Services (AWS) public cloud. In case of disaster, Disaster Recovery ensures business continuity without the need for additional dedicated on-premise software, storage or hardware, which in turn ensures a significant reduction in cost and improvement in agility.
The virtual machine can be recovered on-demand in the cloud. Thus system downtime and its resulting impact on productivity are reduced to minutes.
The following diagram provides an overview of the architecture:
Watch the following video to know more about Disaster Recovery solution.
Benefits of Druva disaster recovery over traditional disaster recovery
Disaster Recovery provides a wide array of benefits to maintain business continuity during unplanned disasters that may disrupt the VMware environment. To ensure proper failover when disaster strikes your environment, Disaster Recovery provides an on-demand, cost-effective solution to eliminate the infrastructure burden, and significantly reduce the downtime.
| Aspect | Disaster Recovery | Traditional disaster recovery |
|---|---|---|
| Cost |
Cost-effective Disaster recovery site based on public cloud infrastructure such as AWS, drastically reduces the overall CAPEX of implementing a DR solution, thereby making it accessible to organizations, which previously had no disaster recovery strategy in place due to costs involved in the traditional setup. |
Expensive The traditional disaster recovery setup comprises a secondary physical disaster recovery site that involves huge upfront CAPEX. It also requires an identical hardware system and software patches as that on the primary site that make the entire proposition of maintaining a secondary site cost-prohibitive. |
| Geographical reach for disaster recovery |
Enables extensive geographical reach Owing to the public cloud infrastructure, the location of the disaster recovery site can now be as far as across continents from the primary site. |
Limits geographical reach for disaster recovery Disaster recovery site cannot span more than 30-60 miles away from the primary site, which is insufficient for coherent disaster recovery planning where customers want more protection than just a few miles and for a few critical applications. |
| Development and test use |
Preconfigure failover settings Disaster Recovery workflow allows administrators to preconfigure failover settings such as VPC, subnet, security groups, and IP assignment, making actual failover a simple one-click operation. Easy setup of the Development/Test lab environments Disaster Recovery facilitates easy setup of the Development/Test lab environments that are identical to the production systems. It also eliminates the overhead of setting up labs in traditional data centers. |
The traditional disaster recovery requires IT expertise to perform complex processes for disaster recovery testing. |
| Disaster recovery site failure |
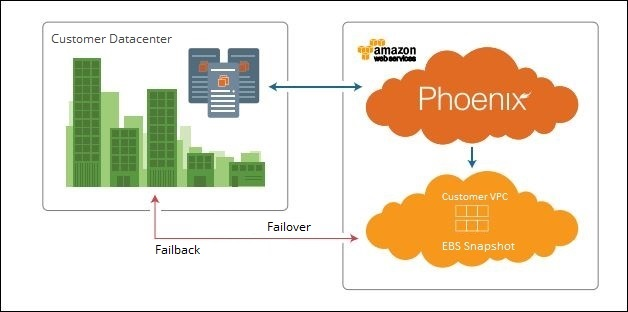
Automated disaster recovery sites: Disaster Recovery provides automated disaster recovery sites that are brought online in a few minutes, which avoids data loss and ensures business continuity. Robust failback Disaster Recovery enables administrators to recover virtual machines with a single click in the data center and thus reduces the need of a managed DR site, onsite hardware, and heavy administration and maintenance. |
Additional cost may incur to start operations at the disaster recovery site in case of disaster recovery site failure. It may jeopardize data and business continuity. |

