How to associate elastic IPs detached after DR
Overview
What is an Elastic IP?
An Elastic IP address is a static public IPv4 address designed for dynamic cloud computing and is associated with your AWS account. If your instance does not have a public IPv4 address, you can associate an elastic IP address with your instance to enable communication with the internet, such as to connect to your instance from your local computer.
With an Elastic IP address, you can mask the failure of an instance or software by rapidly remapping the address to another instance in your account.
How CloudRanger handles elastic IPs during DR?
CloudRanger cannot copy elastic IPs as they are globally unique across the internet. Also, AWS does not support moving Elastic IPs. Elastic IPs are specific to a VPC and are confined to a region. As elastic IPs are region-specific, they cannot be allocated to a DR instance spawned in a separate region.
For each elastic IP associated with a VPC, CloudRanger creates an equivalent IP in a cloned VPC. Therefore, you logically get the same number of IPs and despite being different, they are used in the same places.
Therefore, when you use an allocated elastic IP to perform DR of EC2, the elastic IPs used by individual DR servers are unassociated after DR.
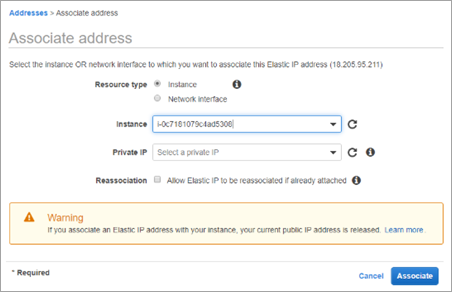
Associate elastic IPs detached after DR
The allocated detached elastic IPs must be associated with their respective servers after DR from AWS console using the below steps.
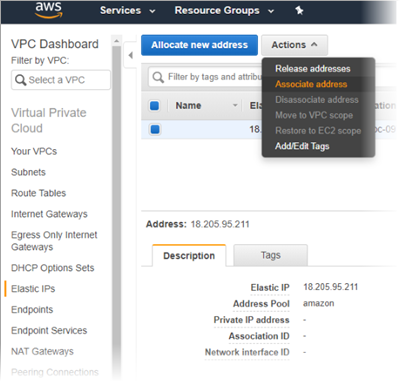
- Go to VPC > Elastic IPs.
- Select the required IP > Actions> Associate address.
- Select the required instance and select Associate.