Configure AWS Recycle Bin
The availability of this feature is by default limited only to customers with Enterprise and Elite licenses.
To get started with AWS Recycle Bin, you will first need to configure your resources using appropriate tags. Once resources are identified, all associated snapshots will continue to reside in recycle bin based on the pre-defined retention criteria. You may choose to retrieve these snapshots within the retention period, right from your management console.
Considerations
Business implications to consider when configuring AWS Recycle BIn:
- Storage costs on retention of deleted snapshots
- Security considerations associated with storing business-critical snapshots
- Compliance and governance on retention
Overall workflow
Step 1: Define retention rules in AWS
To enable and use Recycle Bin, you must create retention rules in the AWS Regions in which you want to protect snapshots. Retention rules specify the following:
- The snapshots to be retained in Recycle Bin once they are deleted
- The retention period for which to retain snapshots in the Recycle Bin post deletion
With Recycle Bin, you can create two types of retention rules:
- Tag-level retention rules: Use resource tags to identify the snapshots that are to be retained in the Recycle Bin. For each retention rule, specify one or more key:value pairs. Snapshots tagged with at least one tag key and value pairs, which are also specified in the retention rule, are automatically retained in the Recycle Bin upon deletion. Use tag-based retention rules to protect specific snapshots in your account based on their tags.
- Region-level retention rules: These retention rules do not have any resource tags specified. They apply to all snapshots in the Region in which they are created, even if the snapshots are not tagged. Use this type of retention rule if you want to protect snapshots within a specific AWS Region.
Snapshots continue to reside in the Recycle Bin until one of the following happens:
- You manually restore it for use. When you restore a snapshot from the Recycle Bin, the snapshot is removed from the Recycle Bin and it immediately becomes available for use as a regular snapshot. You can use restored snapshots in the same way as any other snapshot in your account.
- The retention period expires. If the retention period expires, and the snapshot has not been restored from the Recycle Bin, the snapshot is permanently deleted from the Recycle Bin and it can no longer be viewed or restored.
Create retention rules
To create a retention rule, you must specify the Resource Type and the resource tags to identify the snapshots to be retained. The retention rules function only in the Regions in which they are created. For detailed steps on creating retention rules from your AWS console, refer to the AWS documentation.
Step 2: Using tags to configure Recycle Bin
To enable Recycle Bin, you will need to set up tags to configure resource orchestration. Tags are standardized, case-sensitive key-value pairs that act as metadata to help identify and organize your AWS resources. Use the Add Tags feature to specify the key and the associated value to manage resource orchestration.
- Log into your Druva CloudRanger console and navigate to Resources > EBS.
- Select a resource and then click Add Tags.
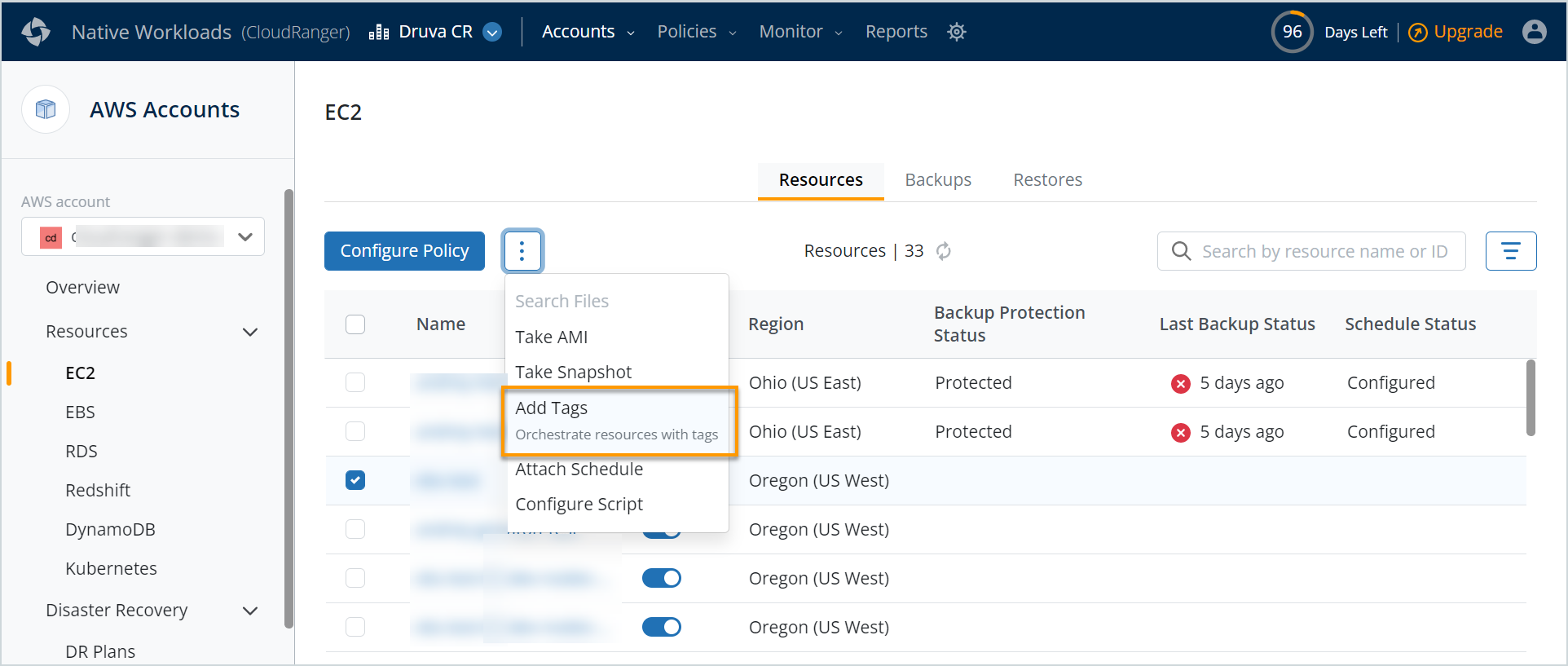
- Define tags with an appropriate Key and associate a relevant Value depending on the selected key. For example:
Key: Origin; Value: Origin ID
Key: Region; Value: us-east
Key: Created by Policy; Value: New Policy - Click Save.
Best Practices
Consider a scenario where the retention settings are configured in AWS, and the tags for Recycle Bin are defined only for AMIs but not for snapshots.
In case of accidental deletion, the snapshots are deleted while AMI moves to Recycle Bin. However, the AMI would still be unrecoverable from Recycle Bin since the snapshots are no longer available. This is because the snapshot IDs in the case of EBS volumes are used as part of the root block device mappings for the AMI.
What you can do
- Retention on AWS: As a best practice, it is recommended to enable Region-level retention or set a generic tag with a default retention set and have all the volumes tagged with the key-value pair. This ensures that snapshots would continue to move to Recycle Bin thus enabling the recovery of snapshots within the retention period defined.
- Configuration on management console:
- Define an identical tag for both the EBS snapshots and the AMI from your AWS console.
- Navigate to the management console and create or edit the corresponding backup policy.
- On the Additional Options tab, under Add Tags to Backups specify the tags to be applied to each backup generated by the policy. Based on the Key selected, you will need to specify the appropriate Value. For example:
Key: Created by Policy; Value: New
Key: Origin; Value: Specify Origin ID - Select the Inherit tags from Source checkbox to inherit or retrieve tags from the Origin servers and apply them to backups generated by the policy.

